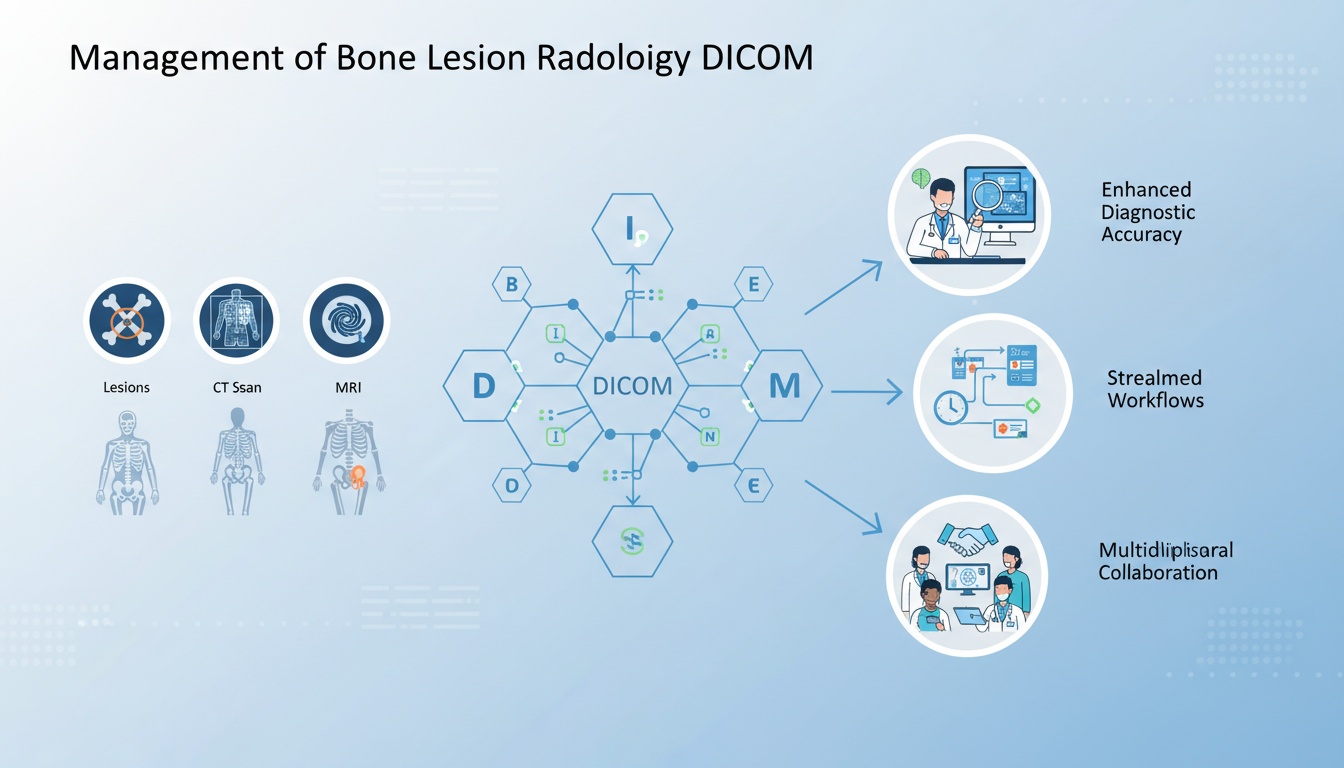
Bone lesion radiology can be challenging to diagnose and manage. It often requires detailed imaging from multiple modalities, such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs. Accurate imaging is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment planning.
Enter DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) standards—a revolutionary framework that ensures seamless interoperability and integration of medical images across various devices and platforms.
Since its inception, DICOM has transformed medical imaging, allowing healthcare providers to manage and share bone lesion images efficiently. This enhances diagnostic accuracy, streamlines workflows, and fosters collaboration among multidisciplinary teams.
In this blog post, we will share the pivotal role of DICOM standards in managing bone lesion images, highlighting how they ensure compatibility, improve efficiency, and ultimately elevate patient care.
Stay put as we explore DICOM's significant impact on radiology and its ongoing evolution in medical imaging.
Bone lesions refer to abnormal growths or areas of damaged tissue within the bones. Their nature and implications vary widely, ranging from benign (non-cancerous) to malignant (cancerous) conditions.
Understanding the types and causes of bone lesions is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Benign Lesions: These include conditions like osteochondromas (bone and cartilage growths), bone cysts, and fibrous dysplasia. Benign lesions are generally non-cancerous and may not always require aggressive treatment.
Malignant Lesions: These cancerous growths can spread and cause significant health issues. Examples include osteosarcoma, Ewing's sarcoma, and metastatic bone disease, where cancer spreads from other parts of the body to the bones.
Genetic Factors: Some bone lesions, like certain benign tumors, can be linked to genetic conditions.
Infections: Osteomyelitis, an infection of the bone, can cause destructive bone lesions.
Trauma: Injuries can lead to the development of bone cysts or areas of abnormal healing.
Cancer: Both primary bone cancers and secondary (metastatic) cancers can cause bone lesions.
Accurate and detailed imaging is vital for the effective diagnosis, treatment planning, and management of bone lesions. Here’s why imaging plays such a crucial role:
Imaging helps early detection of bone lesions, which is essential for successful treatment outcomes. Early diagnosis can differentiate between benign and malignant lesions, guiding appropriate therapeutic strategies.
Detailed imaging allows radiologists to characterize the lesion accurately, determining its size, shape, location, and effect on surrounding tissues. This characterization is critical in determining the lesion's nature.
Imaging provides surgeons with a clear roadmap for lesions requiring surgical intervention. It helps in planning the extent of surgery needed, ensuring precision and reducing the risk of complications.
Imaging monitors the response to chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or surgery treatments. It helps assess whether the lesion is shrinking, stable, or progressing.
Regular imaging follow-ups are essential for patients with bone lesions to track any changes over time. This is especially important for malignant lesions to detect recurrences early.
Advanced imaging techniques enable minimally invasive procedures like image-guided biopsies or radiofrequency ablation, offering alternatives to traditional surgery with reduced recovery times.
DICOM, which stands for Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine, is a comprehensive standard used in medical imaging to ensure the interoperability and seamless exchange of images and related information across different imaging devices and systems. Established by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) and the American College of Radiology (ACR), DICOM is crucial in the medical field for creating, storing, transmitting, and displaying medical imaging information.
DICOM ensures that medical images and associated data can be shared across various equipment and systems, regardless of the manufacturer. This standardization is essential for integrating imaging devices such as X-rays, MRI, CT scanners, and PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication Systems).
DICOM maintains the quality and integrity of medical images, ensuring that the images are accurate and reliable for diagnosis and treatment planning.
By standardizing communication protocols, DICOM streamlines workflows, reducing the need for manual intervention and allowing for quicker, more efficient handling of medical images.
Before the DICOM, medical imaging systems were often proprietary, with limited vendor equipment compatibility. This created significant challenges for healthcare providers, who needed to integrate various types of imaging technology.
In the early 1980s, the ACR and NEMA collaborated to address these interoperability issues, creating the first version of DICOM. Initially known as ACR/NEMA 300, the standard focused on establishing a protocol for the digital exchange of medical images.
Released in 1993, DICOM 3.0 marked a significant milestone in the standard's development. This version introduced extensive improvements, including support for a wider range of imaging modalities and enhanced image storage, transfer, and display capabilities. It became the foundation for modern DICOM standards.
Over the years, DICOM has evolved to support new imaging modalities and technologies, including ultrasound, nuclear medicine, and digital mammography. Each update has expanded the standard's scope and functionality to keep pace with advancements in medical imaging.
As healthcare increasingly adopts electronic health records, DICOM has evolved to facilitate better integration with EHR systems. This integration ensures that imaging data can be seamlessly incorporated into a patient's complete medical record, improving accessibility and continuity of care.
With growing concerns about data security and patient privacy, DICOM standards have incorporated more robust security measures. These include encryption, secure data transmission protocols, and access control mechanisms to protect sensitive medical information.
Recent updates to DICOM have focused on leveraging web-based technologies, allowing for easier access to medical images through web browsers and mobile devices. This evolution supports telemedicine and remote consultations, making high-quality healthcare more accessible.
Artificial Intelligence Integration: As AI becomes more prevalent in medical imaging, future iterations of DICOM are expected to include standards for AI-generated data and workflows, further enhancing diagnostic accuracy and efficiency.
Cloud Computing: The shift towards cloud-based PACS systems will likely drive further updates to DICOM standards, optimizing them for cloud storage and processing.
The standardization and compatibility provided by DICOM standards are foundational to the interoperability of medical imaging systems. DICOM enhances collaborative care, improves workflow efficiency, and supports the creation of comprehensive patient records by ensuring that devices and software from different manufacturers can work together seamlessly.
One of the primary objectives of DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) standards is to ensure interoperability among medical imaging devices and software from different manufacturers.
This standardization is crucial for the seamless exchange and integration of medical images across various platforms, enhancing healthcare delivery's efficiency and effectiveness.
Uniform Protocols: DICOM defines a set of protocols for formatting and exchanging medical images. These protocols include specifications for file formats, communication methods, and data structures, ensuring that all DICOM-compliant devices and software adhere to the same rules.
Consistent Data Representation: DICOM standardizes how imaging data is represented, including metadata such as patient information, image acquisition parameters, and study details. This consistency ensures that different systems can accurately interpret and use the data.
Vendor Neutrality: By adhering to DICOM standards, manufacturers can ensure that their devices and software are compatible with other vendors. This vendor-neutral approach prevents proprietary silos, where imaging data can only be accessed and used within a single manufacturer’s ecosystem.
Extensibility: DICOM is designed to be extensible, allowing for the inclusion of new imaging modalities and technologies as they emerge. This adaptability ensures that the standard remains relevant and can accommodate future advancements in medical imaging.
Compatibility is paramount in medical imaging, particularly in multidisciplinary care settings where various specialists need access, review, and interpret images. DICOM standards are critical in ensuring this compatibility, facilitating collaborative care, and improving patient outcomes.
Multi-Disciplinary Collaboration: Patients often require the expertise of multiple healthcare professionals, including radiologists, surgeons, oncologists, and primary care physicians. DICOM compatibility ensures that imaging data can be easily shared and accessed by all relevant specialists, regardless of the devices or software they use. This seamless sharing enhances collaborative diagnosis and treatment planning.
Comprehensive Patient Records: Maintaining comprehensive and integrated patient records is essential for high-quality care in modern healthcare. DICOM standards ensure that imaging data can be integrated with other clinical information systems, such as electronic health records (EHRs), creating a unified and accessible patient record. This integration supports continuity of care and informed decision-making.
Workflow Efficiency: Compatibility facilitated by DICOM standards streamlines workflows within healthcare facilities. Images can be quickly transferred between departments, reducing delays in diagnosis and treatment. For example, an orthopedic surgeon can promptly review MRI scans from radiology, or an oncologist can access PET scans to plan cancer treatment, all within a standardized system.
Patient Mobility: DICOM compatibility also benefits patients who receive care from multiple providers or move between different healthcare systems. Standardized imaging data can be easily transferred and accessed, ensuring that patients receive consistent and informed care regardless of where they are treated.
Reduced Redundancy: DICOM standards reduce the need for redundant imaging studies by ensuring compatibility. When previous images are readily accessible and compatible with new systems, healthcare providers can avoid unnecessary repeat scans, reducing patient exposure to radiation and lowering healthcare costs.
In a hospital setting, DICOM ensures that imaging devices such as CT scanners, MRI machines, and ultrasound units can all communicate with the central PACS system. This integration allows for efficient storage, retrieval, and viewing of images, supporting diagnostic accuracy and timely patient care.
In telemedicine applications, DICOM compatibility enables remote radiologists to access and interpret imaging studies from different locations. This capability is particularly valuable in rural or underserved areas, where access to specialist care may be limited.
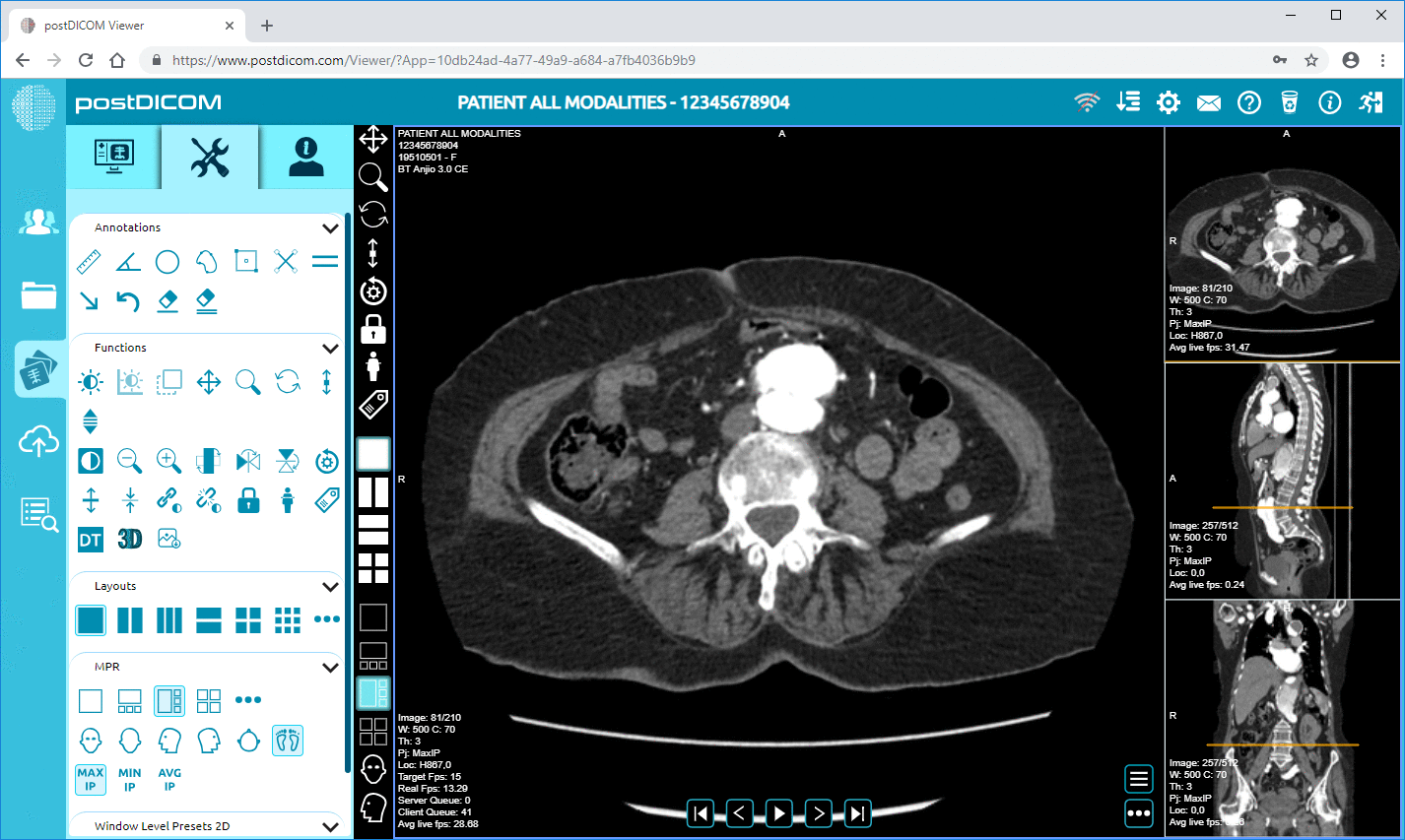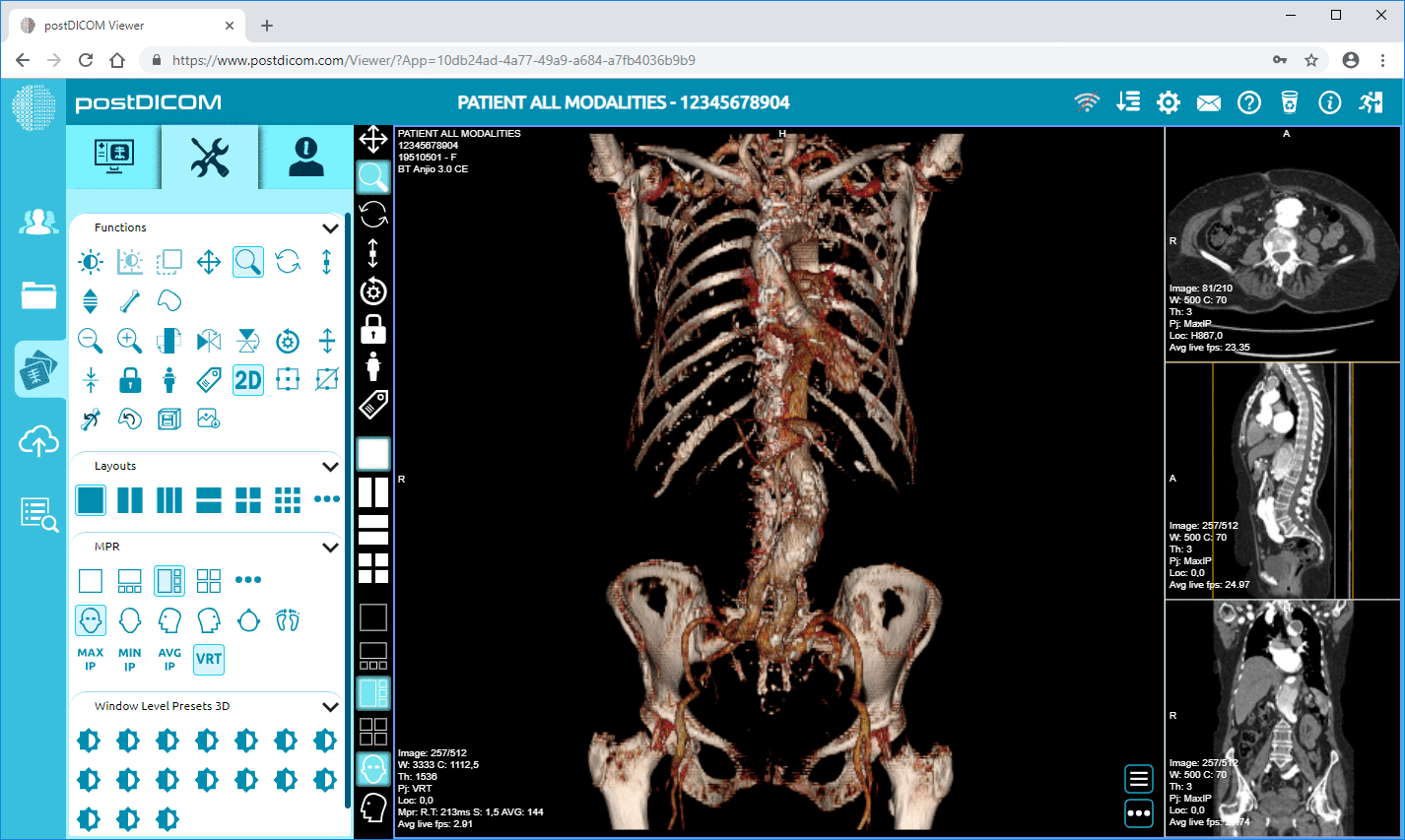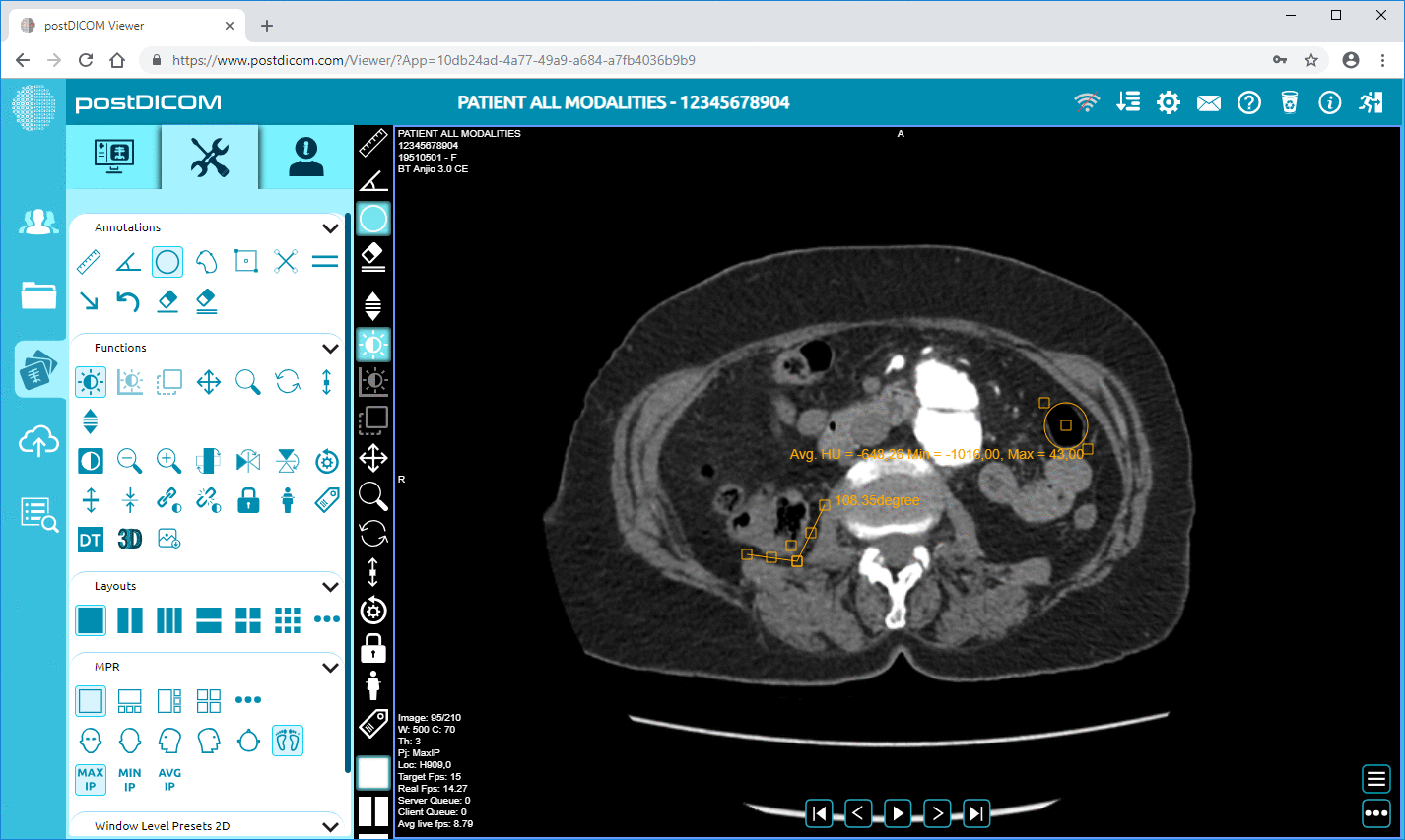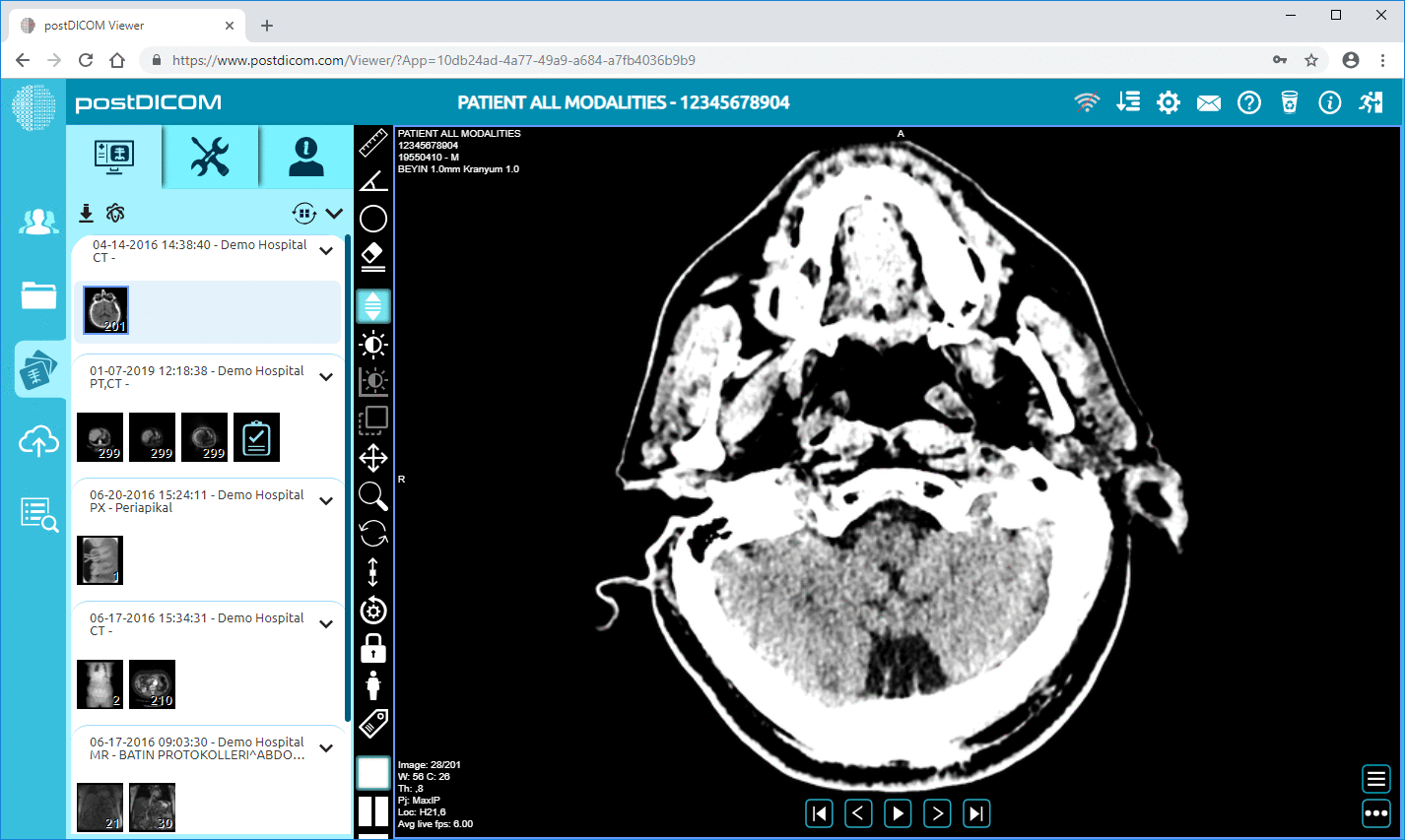
The seamless integration of images from different modalities into a unified system, facilitated by DICOM standards, is essential for comprehensive bone lesion assessment. This integration ensures that healthcare providers have access to a complete imaging data set, enabling accurate diagnosis, effective treatment planning, and improved patient outcomes.
Bone lesions often present complex diagnostic challenges that require using multiple imaging modalities to understand the lesion's characteristics and implications comprehensively. Different imaging techniques provide unique insights, making a multi-modality approach crucial for accurate assessment and effective treatment planning.
X-ray: X-rays are typically the first imaging modality to detect bone lesions. They provide a quick and effective way to visualize bone structure and identify abnormalities such as fractures, cysts, or tumors.
CT (Computed Tomography): CT scans offer detailed cross-sectional images of the bone and surrounding tissues. They are handy for evaluating a lesion's size, shape, extent, and relationship to nearby structures.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): MRI provides high-resolution images of soft tissues, making it invaluable for assessing bone marrow involvement and the soft tissue components of a lesion. Based on tissue characteristics, MRI can differentiate between benign and malignant lesions.
PET (Positron Emission Tomography): PET scans are often used with CT or MRI to assess metabolic activity and identify malignant lesions. They help stage cancer and evaluate the effectiveness of treatments.
Bone Scintigraphy (Bone Scan): This nuclear medicine technique detects areas of increased bone metabolism, indicating lesions. It is beneficial for identifying metastatic disease.
Combining these modalities provides a comprehensive assessment of bone lesions, enabling clinicians to make more informed diagnostic and treatment decisions.
Integrating multiple imaging modalities into a unified system is essential for providing a holistic view of a patient’s condition. DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) standards are pivotal in facilitating this integration, ensuring that images from various modalities can be seamlessly managed and accessed.
Standardized Data Format: DICOM defines a universal format for storing and transmitting medical images. This standardization ensures that images from different modalities, such as X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and PET scans, can be stored consistently. This uniformity is critical for integrating diverse imaging data into a single system.
Cross-Modality Compatibility: DICOM standards support the compatibility of imaging data across various devices and software. This means that images acquired from different imaging modalities can be easily incorporated into the same PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System) without compatibility issues. Clinicians can access a comprehensive set of images from a single platform.
Holistic Patient View: Unified image management enables healthcare providers to view and compare images from different modalities side by side. This holistic view is crucial for accurately assessing bone lesions, as it allows for correlating findings from other imaging techniques. For example, a CT scan might reveal the precise anatomy of a lesion, while an MRI might provide information about its soft tissue characteristics, and a PET scan might show metabolic activity.
Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy: DICOM standards help improve diagnostic accuracy by integrating images from multiple modalities. Radiologists can cross-reference different imaging findings to form a more complete and nuanced understanding of the lesion. This integrated approach reduces the likelihood of misdiagnosis and ensures that all relevant information is considered in the diagnostic process.
Streamlined Workflows: Unified image management facilitated by DICOM standards streamlines clinical workflows. Healthcare providers can access all necessary images through a single interface, reducing the time spent switching between systems or retrieving images from disparate sources. This efficiency is critical in busy clinical settings where timely diagnosis and treatment are crucial.
Collaboration and Communication: DICOM’s standardized image management approach enhances multidisciplinary team collaboration. Specialists from different fields can easily share and discuss imaging findings, fostering a collaborative environment that improves patient care. For example, a radiologist, orthopedic surgeon, and oncologist can all access and review the same images, ensuring their combined expertise informs the treatment plan.
Advanced Image Analysis: Unified systems that adhere to DICOM standards often incorporate advanced image analysis tools. These tools can perform functions such as 3D reconstruction, image fusion, and quantitative analysis, providing deeper insights into the characteristics of bone lesions. This advanced analysis supports more precise and personalized treatment planning.
 - Created by PostDICOM.jpg)
As medical imaging technology evolves, so must the standards underpinning it. DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) standards have long been the backbone of medical image management, and several emerging technological advancements promise to enhance the management of bone lesion images further.
AI-Powered Analysis: AI and machine learning algorithms can increasingly rapidly analyze medical images. Future iterations of DICOM standards could incorporate AI-generated metadata and analysis results, enabling more automated and accurate detection, classification, and monitoring of bone lesions.
Decision Support Systems: By integrating AI into the DICOM framework, radiologists can receive real-time decision support, highlighting areas of concern, suggesting potential diagnoses, and recommending follow-up actions based on the analysis of bone lesion images.
High-Resolution Imaging: Advances in imaging technology are producing ever-higher-resolution images. Future DICOM standards must support these more extensive, more detailed files without compromising performance or storage efficiency.
Advanced Compression Techniques: Improved compression algorithms could be standardized within DICOM to reduce file sizes while maintaining image quality, facilitating faster transmission, and more efficient storage of bone lesion images.
Three-Dimensional Imaging: As 3D imaging becomes more prevalent, DICOM standards will evolve to better handle the storage, transmission, and display of 3D models. This is particularly relevant for complex bone lesions, where 3D visualization can provide significant diagnostic and surgical planning advantages.
Four-Dimensional Imaging: Incorporating time as a fourth dimension, 4D imaging allows for visualizing changes over time. This could be critical in monitoring the progression or regression of bone lesions, assessing treatment effectiveness, and planning future interventions.
Cloud Integration: Future DICOM standards will likely further enhance compatibility with cloud-based PACS systems. This will facilitate secure, remote access to bone lesion images, supporting telemedicine and remote consultation services.
Real-Time Collaboration: Enhanced support for real-time collaboration tools within DICOM will allow multiple healthcare professionals to work on the same set of images simultaneously, regardless of their location, improving the quality and timeliness of patient care.
The field of medical imaging is dynamic, with constant advancements and emerging technologies that continually push the boundaries of what is possible. Continuous improvement and adaptation are essential for DICOM standards to remain relevant and effective.
Meeting Evolving Needs: As new imaging modalities and technologies emerge, DICOM standards must be updated to incorporate these innovations. This ensures that the standard remains comprehensive and applicable to all types of medical imaging, including the latest advancements in bone lesion radiology.
Enhancing Interoperability: Continuous improvement helps maintain and improve interoperability across different systems and devices. By regularly updating DICOM standards, the industry can ensure that new technologies and old systems communicate seamlessly, facilitating the smooth integration of cutting-edge tools into existing workflows.
Improving Efficiency: Ongoing enhancements to DICOM standards can streamline workflows, reduce manual intervention, and improve the efficiency of image management processes. This includes optimizing data handling, storage, and retrieval processes to keep pace with medical imaging data's increasing volume and complexity.
Addressing Security and Privacy: With growing concerns about data security and patient privacy, continuous improvement of DICOM standards is crucial for incorporating the latest security measures. This includes encryption, secure transmission protocols, and robust access controls to protect sensitive medical information.
Supporting Regulatory Compliance: Healthcare regulations and standards are continually evolving. Regular updates to DICOM ensure it remains compliant with the latest legal and regulatory requirements, helping healthcare providers meet their obligations and avoid potential legal issues.
Encouraging Innovation: By staying at the forefront of technological advancements, DICOM standards can encourage and facilitate innovation within the medical imaging industry. This can lead to development of new tools, techniques, and applications that improve the diagnosis, treatment, and management of bone lesions and other medical conditions.
The future of DICOM in bone lesion radiology is promising, with numerous advancements that will further enhance the management of medical images.
By integrating cutting-edge technologies such as AI, 3D and 4D imaging, and cloud-based solutions, DICOM standards will continue to evolve, providing a robust framework for the future of medical imaging.
Continuous improvement and adaptation are essential to ensure that DICOM remains relevant and effective, meeting the ever-changing needs of healthcare professionals and ultimately improving patient care.
As these advancements unfold, the role of DICOM in facilitating high-quality, efficient, and secure medical imaging will become even more critical, paving the way for innovations and better healthcare outcomes.
|
Cloud PACS and Online DICOM ViewerUpload DICOM images and clinical documents to PostDICOM servers. Store, view, collaborate, and share your medical imaging files. |