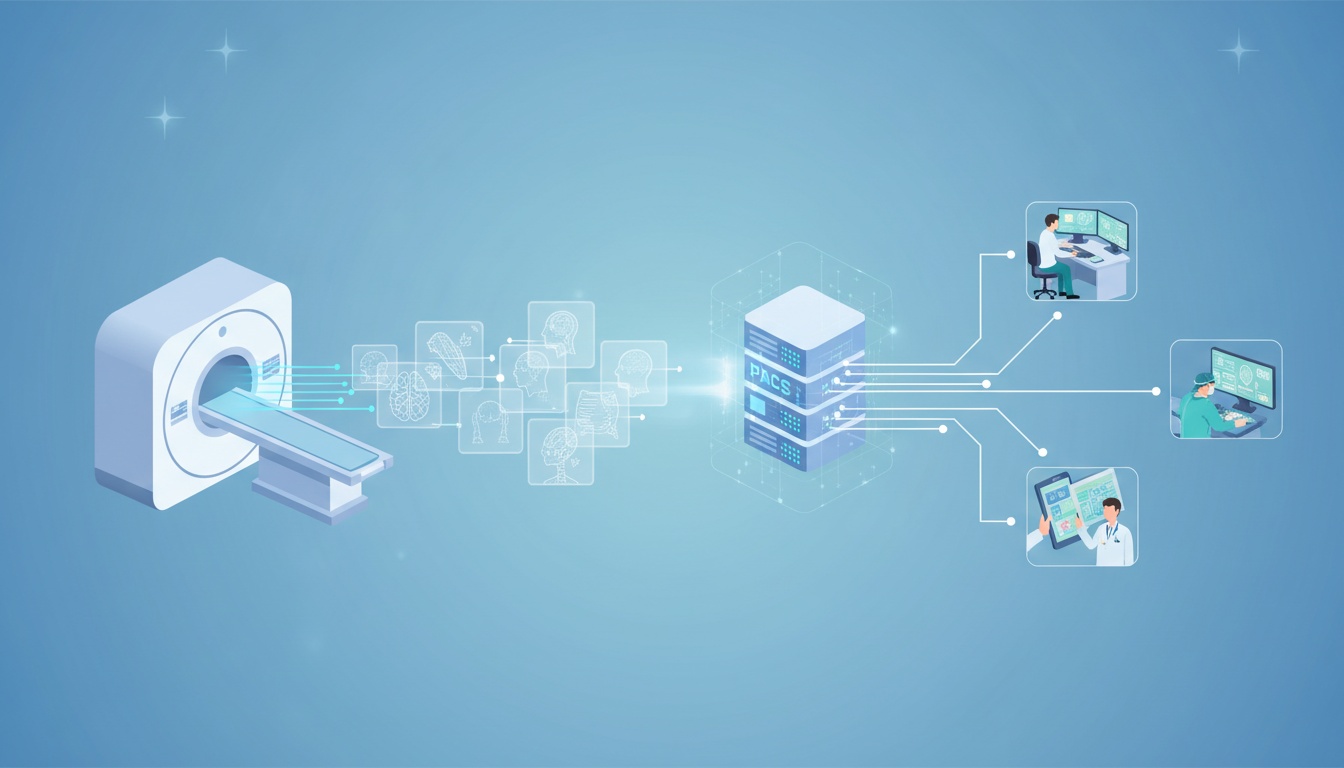

Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a cornerstone of modern medical diagnostics, providing detailed images vital for accurate diagnosis and treatment. Equally essential is the Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS), which revolutionizes how these critical images are managed and accessed within healthcare settings.
This blog explores the seamless integration of MRI with PACS. This synergy enhances radiology departments' functionality and propels the medical workflow toward greater efficiency and effectiveness.
By bridging the technical capabilities of MRI with the robust data management of PACS, healthcare providers can offer faster, more precise diagnoses, ensuring timely and improved patient care.
Join us as we delve into how this vital link streamlines radiology workflows, turning sophisticated imaging technology into an everyday tool for saving lives and enhancing health outcomes.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a sophisticated diagnostic tool critical in modern medicine. Unlike X-rays or CT scans, MRI uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the inside of the body.
This technique is particularly effective for visualizing soft tissues, including the brain, muscles, heart, and cancers. MRI is invaluable not only because it avoids ionizing radiation but also because it can provide clear, precise images that are crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Can EEG see more than MRI when integrated with PACS?
Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS) is a medical imaging technology used primarily for securely storing, retrieving, managing, and sharing digital images produced by various health imaging modalities, including MRI.
PACS allows for a paperless workflow by integrating with other hospital systems, such as Radiology Information Systems (RIS) and Electronic Health Records (EHR). This facilitates a streamlined process that enhances the efficiency of medical diagnoses and treatment. Check how PACS can be the best choice for you.
Integrating MRI data into PACS systems marks a significant advancement in medical imaging technology. This integration allows radiologists and other medical professionals to access, analyze, and compare MRI scans with unprecedented ease and speed. Here’s how MRI data enhances PACS utility:
1. Enhanced Accessibility: With MRI scans stored in PACS, healthcare providers can access vital diagnostic information from any connected workstation within the hospital network or securely from remote locations. This accessibility is crucial for urgent diagnosis and for consultations with specialists, regardless of their physical location.
2. Improved Diagnostic Workflows: The integration allows for more streamlined diagnostic processes. Physicians can pull up historical and current MRI data for side-by-side comparisons to monitor disease progression, make more informed treatment decisions, and discuss cases with multidisciplinary teams without needing physical film or delayed access.
3. Increased Efficiency: PACS systems equipped with MRI capabilities reduce technicians' time managing physical images, thus reducing errors and operational costs. This integration also supports advanced imaging analysis tools for quicker, more accurate interpretations.
Integrating MRI data with Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) significantly enhances the radiology department's capabilities.
This integration brings numerous advantages, from enhancing diagnostic accuracy to improving accessibility and streamlining workflows, fundamentally changing how medical imaging data is handled and utilized.
Integrating MRI scans into PACS systems greatly supports radiologists in their diagnostic processes. PACS provides advanced image viewing tools that allow for detailed examination of MRI scans. Features such as zoom, contrast adjustment, and layer manipulation enable radiologists to assess images more precisely.
Moreover, these systems often come with software that can help identify patterns and anomalies, potentially highlighting areas of concern that may require closer inspection.
This technology supports a higher diagnostic accuracy and significantly reduces the chances of oversight, ensuring that patients receive the most accurate assessments of their medical conditions.
One of the standout benefits of MRI-PACS integration is the improved accessibility it offers. MRI images stored in PACS can be accessed by various departments within a healthcare facility, allowing for seamless sharing and consultation.
Additionally, these images can be viewed by specialists working offsite, which is particularly advantageous in remote consultations or for facilities that operate within a more extensive healthcare network.
This capability ensures that all relevant healthcare providers have access to critical diagnostic information when needed, facilitating a collaborative approach to patient care that leverages the expertise of multiple specialists.
Integrating MRI with PACS significantly streamlines clinical workflows within healthcare facilities.
By automating many of the manual tasks associated with image handling and data entry, PACS frees radiologists and technicians to focus more on patient care rather than administrative duties.
This integration leads to quicker turnaround times for diagnostic reports, enhancing patient throughput and reducing waiting times.
Furthermore, having a system that automatically organizes and stores MRI data reduces the risk of data loss or misfiling, ensuring that all patient records are up-to-date and readily available for future reference.
Integrating MRI data into existing Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) presents a range of technical challenges.
From compatibility issues to data management and ensuring compliance with health data regulations, each aspect requires careful consideration to ensure a smooth and secure integration process.
Challenge: One of the primary technical challenges in integrating MRI machines with PACS is compatibility. MRI systems often use unique software and formats that may not immediately sync with PACS, designed primarily for a broader range of imaging modalities.
Solution: To overcome these compatibility issues, it's essential to ensure both the MRI systems and the PACS are up-to-date with the latest DICOM standards, which facilitate the integration of various imaging types. Healthcare facilities may need to work with IT specialists and vendors to develop or install middleware solutions that act as translators between MRI formats and PACS, ensuring seamless communication and functionality.
Challenge: Managing the large volumes of data generated by MRI scans is a significant challenge. MRI produces highly detailed images that require substantial storage capacity, fast processing speeds, and robust data retrieval systems within PACS.
Solution: Effective data management strategies involve upgrading PACS storage solutions to accommodate the high data requirements of MRI. Implementing tiered storage can help, where recent or frequently accessed MRI scans are kept in fast, readily accessible storage. In contrast, older scans are archived in more cost-effective, slower storage solutions. Additionally, utilizing data compression techniques without loss of image quality can reduce storage demands while maintaining the diagnostic integrity of MRI images.
Challenge: Ensuring that MRI data within PACS complies with health data regulations and privacy laws is crucial. The integration must protect patient privacy and ensure data security against unauthorized access or breaches.
Solution: It is critical to implement robust security measures, including encryption of data at rest and in transit, strong authentication mechanisms for system access, and detailed audit trails that log all access and modifications to MRI data. Regular security assessments and compliance audits can help identify and mitigate risks timely. Furthermore, working with compliance experts to understand regional regulations like HIPAA in the U.S. or GDPR in Europe ensures that the integration adheres to all legal requirements.
Integrating MRI data into Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) significantly transforms hospital workflows and patient care.
Background: City Medical Center, a leading healthcare facility, recognized the need to enhance its radiology department by integrating MRI data with its existing PACS. The primary goal was to improve diagnostic accuracy and streamline patient care processes.
Compatibility Issues: The hospital's older PACS system initially struggled to handle large MRI files efficiently, leading to slow data retrieval times.
Training: There was a significant learning curve for radiology staff in adapting to the integrated system.
The center upgraded its PACS software to ensure compatibility with the latest MRI technology, focusing on enhancing data throughput and storage capabilities.
Comprehensive training sessions were held for all radiology staff to familiarize them with the new system functionalities.
The integration led to a marked improvement in the speed and efficiency of diagnostic processes. Radiologists were able to access and compare MRI data more quickly, aiding in faster decision-making.
The streamlined workflow reduced patient wait times and increased the number of daily MRI scans that could be processed.
1. Ensure System Compatibility: Before integration, conduct a thorough assessment to ensure that the PACS can handle MRI data both in terms of file size and format. Upgrading to a PACS that supports the latest DICOM standards is often necessary.
2. Prioritize Staff Training: Effective integration depends on the users' ability to operate the system efficiently. Invest in detailed training programs to ensure that all staff members are comfortable with the new system features.
3. Optimize Data Flow: Work on the data architecture to ensure that MRI data flows seamlessly from the imaging machines to PACS. This might involve setting up more direct network connections or using more powerful servers.
4. Implement Robust Data Security Measures: With the integration of critical MRI data into PACS, enhancing data security protocols is essential. Ensure that the system has up-to-date security measures to protect patient information against unauthorized access.
5. Regularly Monitor and Evaluate the System: Continuous monitoring of the integration’s performance is crucial. Regular feedback from staff and periodic system audits can help identify and resolve ongoing issues, ensuring the system remains efficient and effective.
 - Created by PostDICOM.jpg)
The landscape of medical imaging and information systems is on the brink of significant transformations, driven by advances in technology and expanding applications in healthcare. The integration of MRI with PACS is poised to harness these innovations, promising to redefine diagnostic capabilities and patient care strategies.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: The future of MRI and PACS integration will be heavily influenced by the incorporation of AI and machine learning technologies. AI can revolutionize how MRI data is processed and interpreted within PACS systems. For instance, AI algorithms can automate the detection and characterization of abnormalities in MRI scans, reducing the time radiologists need to spend on each case and potentially increasing diagnostic accuracy. Machine learning models can also learn from vast datasets of MRI images stored in PACS, continuously improving their diagnostic suggestions based on new data.
Enhanced Image Processing: Future developments may include more advanced image processing tools integrated into PACS platforms, capable of providing even more detailed visualizations of MRI data. These enhancements might involve higher-resolution imaging, better 3D reconstructions, and sophisticated rendering techniques that allow doctors to gain deeper insights into patient anatomy and pathologies.
Support for New Clinical Areas: As MRI technology evolves, its integration with PACS is expected to expand into new clinical areas. For example, MRI techniques that allow for functional and molecular imaging could be integrated into PACS, aiding in fields such as neurology, oncology, and cardiology. This integration will facilitate a more holistic view of a patient’s health, not just anatomical but also functional insights, which are crucial for personalized medicine.
Improvements in Telemedicine: The integration of MRI with PACS is also set to enhance telemedicine capabilities. With more robust and secure PACS platforms, MRI images can be easily and securely accessed by specialists around the world, facilitating remote diagnoses and consultations. This is particularly crucial in rural or underserved areas where access to specialist care may be limited. PACS that support real-time sharing and collaboration on MRI data can make telemedicine a more effective tool for delivering expert care remotely.
As we look to the future, the integration of MRI with PACS stands as a beacon of innovation in medical imaging, transforming the landscape of diagnostics and patient care.
The advancements in AI, machine learning, and telemedicine capabilities promise to not only streamline workflows but also elevate the precision and accessibility of medical diagnostics across diverse clinical settings.
For healthcare facilities looking to stay ahead in this technological evolution, choosing a robust and scalable PACS solution is crucial. PostDICOM offers cloud PACS services that are designed to seamlessly integrate with advanced MRI technologies, ensuring that healthcare providers can leverage the full potential of their imaging data.
With PostDICOM, facilities can expect a future-proof system that supports the latest advancements in MRI and PACS integration, enabling them to deliver superior care through more efficient and accurate diagnostics.
Embrace the future of medical imaging with PostDICOM, where cutting-edge technology meets clinical excellence in every scan.
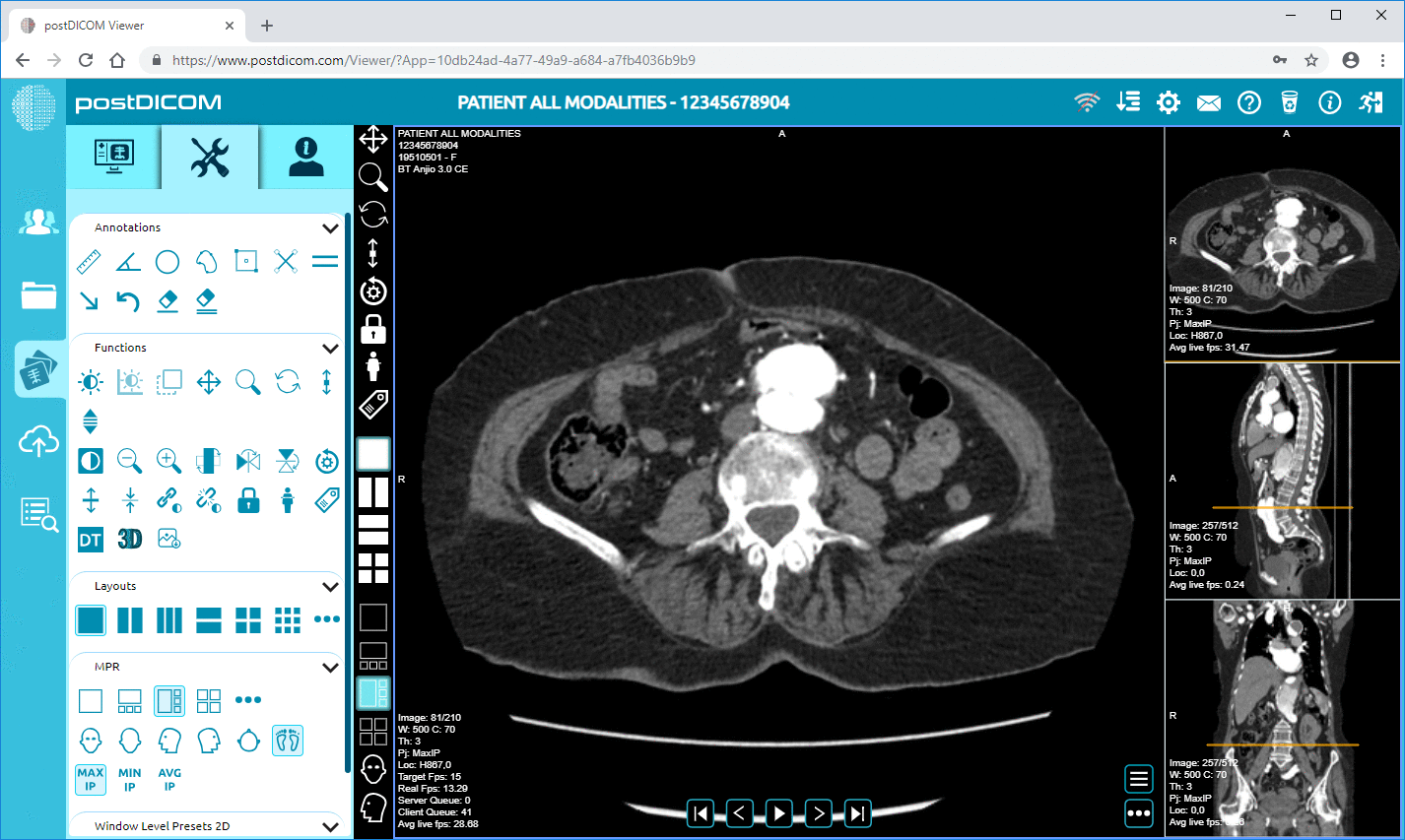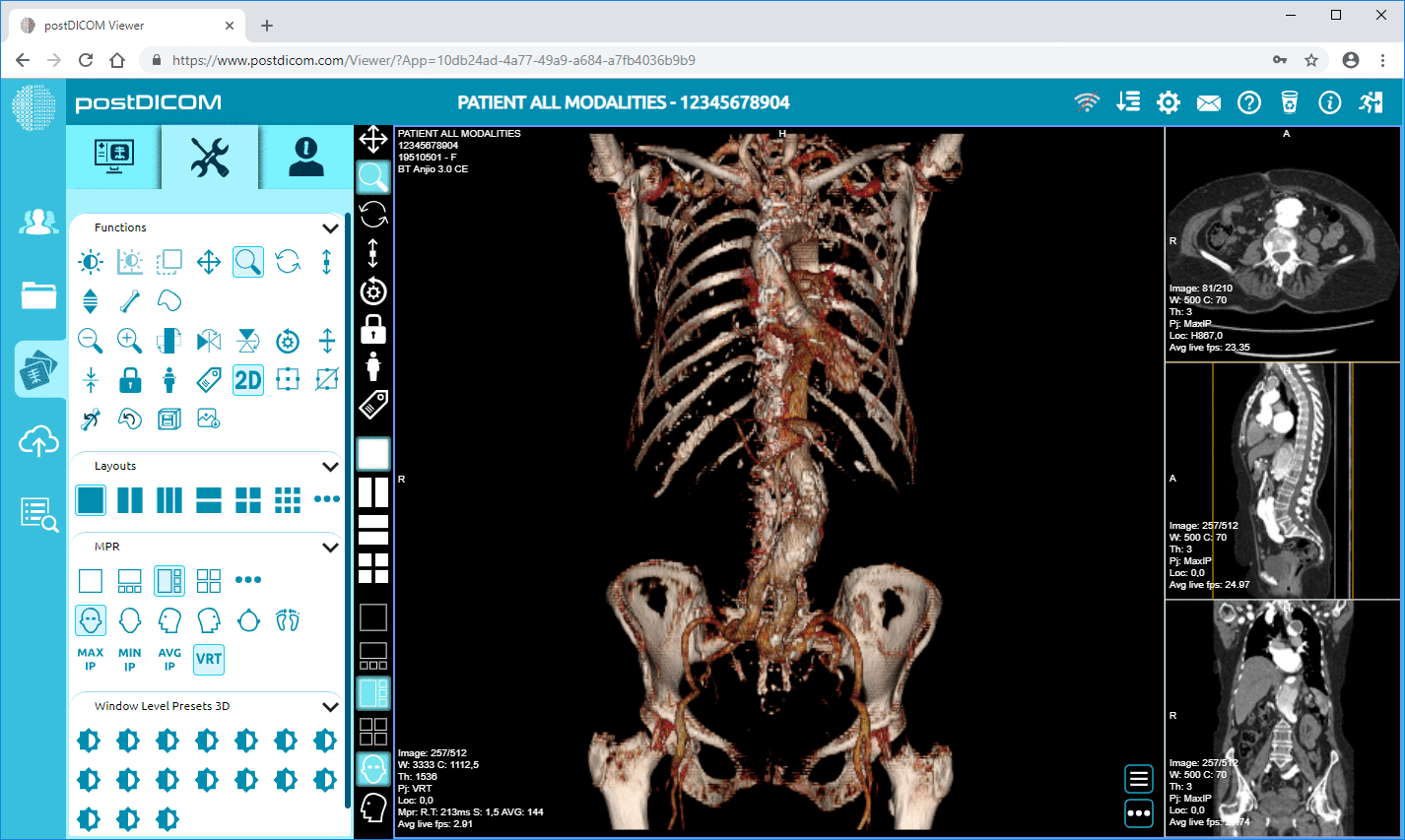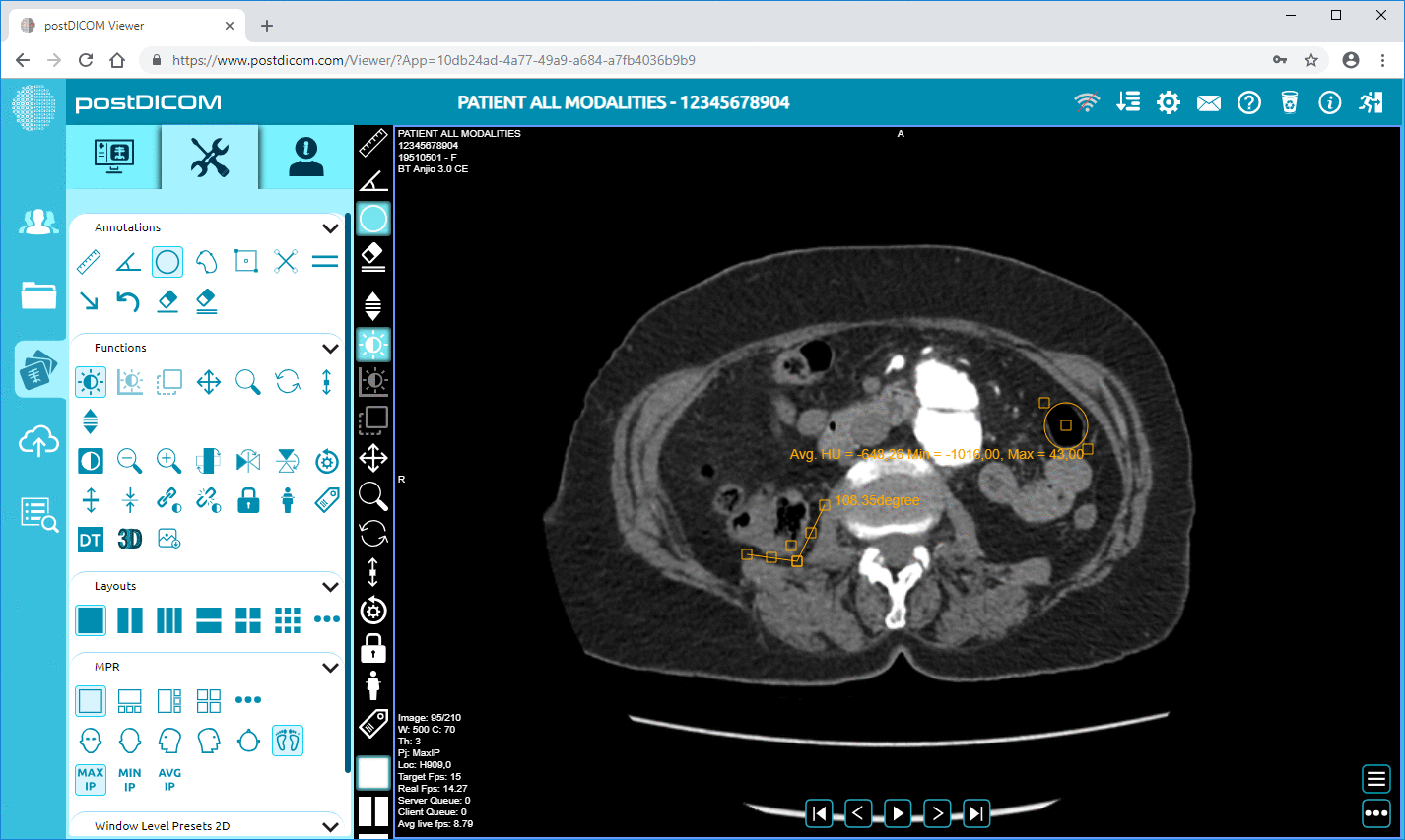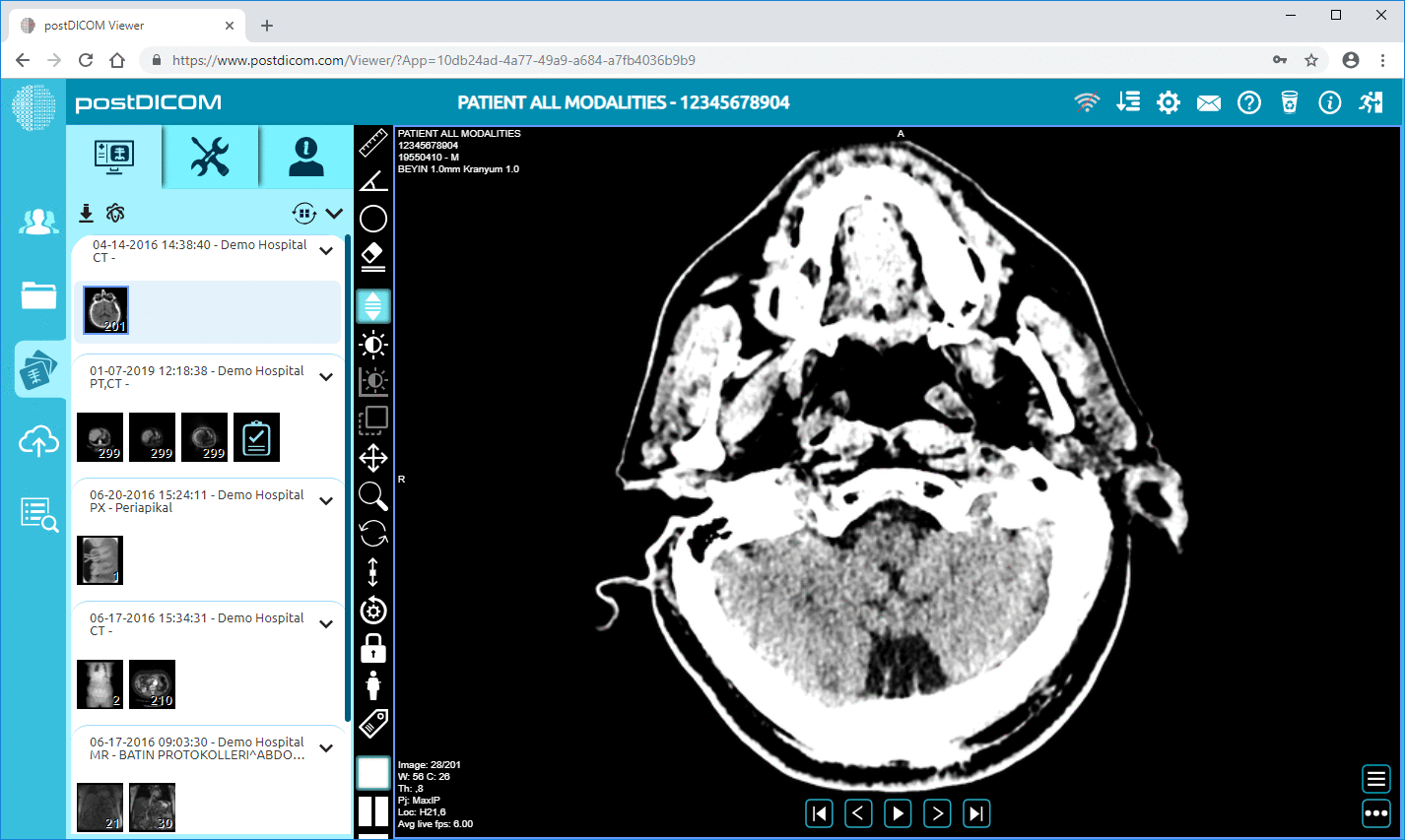
|
Cloud PACS and Online DICOM ViewerUpload DICOM images and clinical documents to PostDICOM servers. Store, view, collaborate, and share your medical imaging files. |